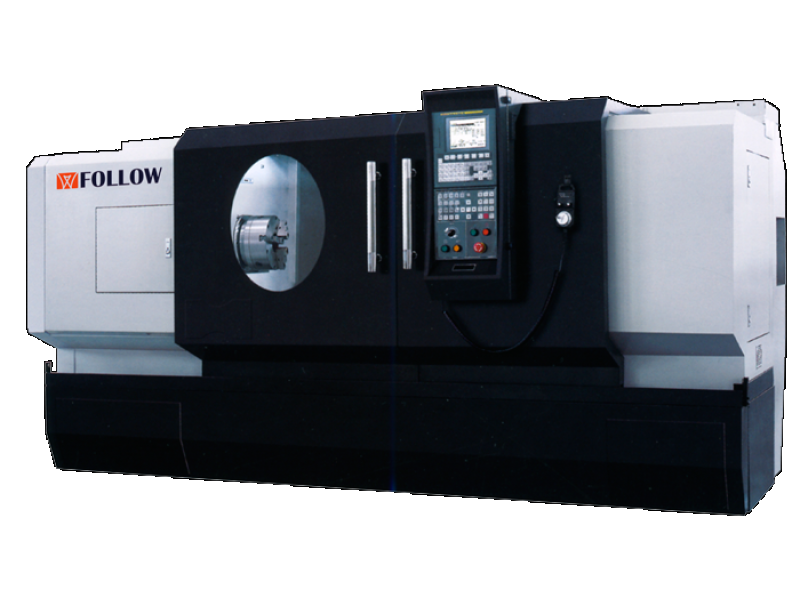
The inclusion of computerized numerical control, CNC, has been a revolution for the metalworking industry. Thanks to this technology, not only are production costs reduced , but also delivery times and labor. The numerical control lathe is a machine tool widely used in machining workshops in various industries thanks to all the advantages it provides for production.
What is a numerical control lathe?
The lathe is the first machine tool to be invented. Its appearance has millenary origin and, over time, it has been adapting to new technologies so as not to fall into disuse. One of them is numerical control. Thanks to this alphanumeric language, lathes work automatically and perform the same operations as manual lathes, but with much more precision, speed and autonomy.
In a numerical control lathe , different cutting tasks (horizontal, vertical or curved) can be carried out in a short period of time and with minimal human intervention. For this, the operator must program the computer integrated in the machine and codify the necessary functions to make the different tools attached to the machine head work.
CNC lathe operation
The numerical control lathe works using the CNC alphanumeric language, previously programmed in the machine’s computer. However, before doing such programming, an expert, generally in engineering and conversational language, must make a design of the part to be worked on using CAD and CAM programs on external computers. Once the design is ready, it is translated into CNC language which works through G-codes.
This language is a type of vectorial programming that collects very simple actions and parameters that the operator configures in the lathe’s computer. For example, figures, line segments, curves, cuts, drilling, etc.; In addition, the machine is provided with the adequate speed to execute said tasks.
Once the design has been entered into the machine, the operator will only need to position the part and clamp it through the lathe’s clamping system and the lathe will do all the work. It will be the lathe itself that chooses the tools it needs to execute the commands that have been entered. On the other hand, it is noteworthy that, today and thanks to collaborative robotics, many lathes allow the coupling of robotic arms or cobots that further reduce labor; because it is precisely these cobots that place the parts in the machines.
Advantages of numerical control lathe
Why use a numerical control lathe? This machine tool does nothing more than provide advantages for machining workshops. The jobs are done with much greater precision and at high speed, which allows mass production; something that does not happen with manual lathes where their operation depends entirely on the strength of the turner.
In addition, on this numerically controlled machine it is possible to work parts with very complex designs and obtain high-quality results, which, if done on a manual lathe, would be very difficult to achieve adequate precision and, furthermore, production costs would be higher.
CNC lathes are very easy to operate and, depending on the number of axes, the operator does not need to manipulate the machine or switch between the different cutting tools; the machine itself is responsible for tilting and manipulating the piece, as it sees fit, to be able to work on its surface at different angles and perspectives.
Numerical Control Lathe Applications
There are different types of CNC lathes on the market and each one performs specific tasks, according to production needs. There are parallel and vertical CNC lathes; copying lathes and even resolution lathes. Thanks to the axes of these machines, the head can move very easily on the piece to be worked and regardless of its shape; therefore, on a numerical control lathe, conical, straight, square, cylindrical, etc. shaped pieces are worked.
These lathes are used to work pieces of great complexity and of very diverse materials: metals (stainless, iron, aluminum); wood or glass, etc. It follows from this that CNC lathes are machine tools that are characterized by their versatility. Not only can they work with various materials, but they can also carry out different machining tasks such as cutting, threading, drilling or drilling, engraving, grooving and turning geometric parts; all these operations are executed in a few minutes, boosting production.
Metalworking is the main industry in which the numerical control lathe is used. In this industry the numerical control lathe is used to give metals a specific shape; later, the pieces will be sent to different industries in turn, such as automotive, manufacturing, food, etc. In metalworking, the main application of CNC lathes is to perform machining by chip removal, as well as drilling and grooving.