Molds and dies are essential parts for mass production lines. They have multiple applications within metalworking for the manufacture of parts, but they are also used in different industries such as food. But, how is the machining of molds and dies carried out?
Uses of molds and dies
Within the production processes, molds and dies play an essential role in the manufacture of parts. For example, the molds are used for injection molding to shape the resin; but they are also used in the foundry to create pieces of different shapes. Here we can find the most varied molds: to make screw heads, to make cans for the canning industry or to create rings in the case of jewelry.
The dies are used, among others, for stamping and to shape metal sheets or plates, as well as to work other shapes with this material. They are also used for the manufacture of automobile parts.
Thanks to the technology that exists today it is possible to create molds and dies , which allows mass production of parts much more easily and that are applied to different industries.
Characteristics of molds and dies
The molds and dies are characterized by having specific, very precise shapes, with an excellent finish and being made with high quality materials. It is important that the materials with which the molds and dies are made can withstand high and low temperatures, since in a mould, for example, molten metals can be poured at high temperatures. That is why it is important that the molds and dies do not deform.
For the manufacture of these parts, steel with high hardness properties is usually used. Hardness not only influences the strength of molds and dies, but also the cutting geometry.
In terms of shape, these tools have a three-dimensional profile, so it is essential that the machines where they are worked have the ability to work 3D surfaces.
What is the matrix?
Tooling is a part of metalworking that, as its name suggests, is responsible for developing techniques for the manufacture of molds and dies (tooling), necessary for the production of serial parts. In die making, the parts are generally manufactured from sheet metal or metal plates and the machining is done without chip removal.
In addition, tooling is also called the work of cutting and deformation of sheets, without chip removal, and using tools called molds and dies. For the elaboration of these tools, as well as the deformation of the sheets, an expert operator in the field is required; This operator is called a toolmaker.
Due to its high production cost, tooling is only recommended for the manufacture of molds and dies of parts in series, since only in this way can the costs of these tools be amortized. However, it should be noted that the tools can be made in a matter of minutes, since the machines in charge of carrying out these processes are capable of manufacturing from 12 to 1,200 pieces per minute.
The tooling is characterized by the low volume of waste generated, since it is not done by chip removal. This allows optimal use of materials; between 75 and 80% of the sheet with which this tool is made is used.
Machining of molds and dies
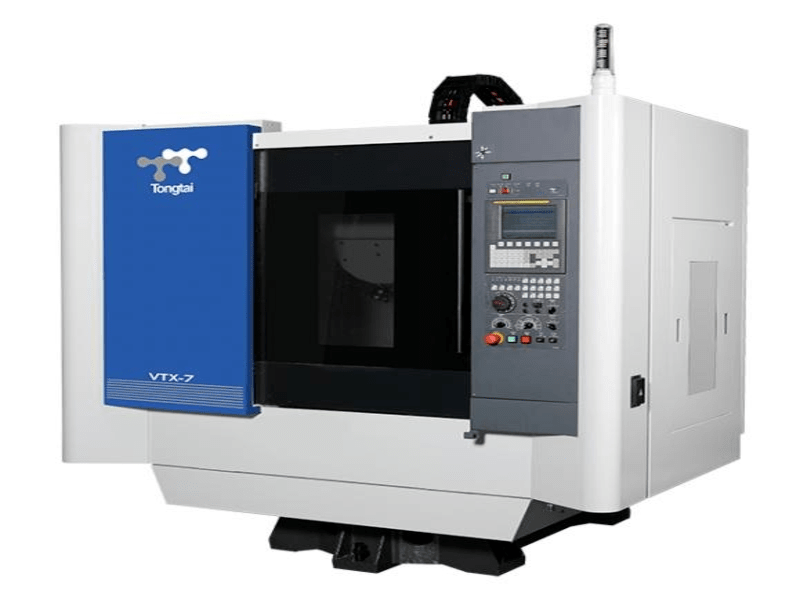
For the creation of molds and dies , different machining techniques are used: turning, milling, drilling, etc.; Of all these, the most common is milling because the pieces have very complex shapes and with various cavities and folds that require very precise work. Hence, it is increasingly common to carry out these processes on multifunction machine tools, capable of combining multiple machining techniques.
Due to the complexity of this tooling, the tooling has been one of the first to adapt to new technologies using advanced software and computerized numerical control machining processes; here we can mention high-speed and high-feed milling. That is why the latest in machine tools is used for the elaboration of these pieces.
Various machining techniques are used to repair these molds and dies that wear out and become damaged over time . This tooling can be repaired using welding, laser treatments or thermal projection of metal; All of these methods are applied directly to the surface of the damaged part. It is important that the machines used both for the manufacture of molds and dies, as well as for their repair, must be advanced cutting tools capable of combining very hard layers of material with other softer ones.